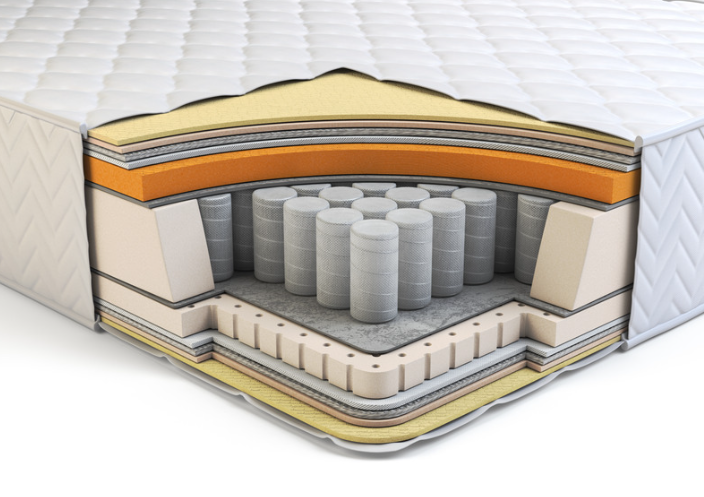
Quality control (QC) is essential for ensuring mattresses maintain their integrity after the rigors of vacuum compression. Inspectors verify the rebound rate to confirm the material returns to its original shape and measure dimensional tolerance to ensure accurate sizing. These critical steps protect product quality and maintain high customer satisfaction. By utilizing specialized testing methods, manufacturers can guarantee their products are reliable and precise.
Key Takeaways
- Mattress quality control ensures products meet strict standards, protecting customer satisfaction and brand integrity.
- Inspectors must allow mattresses to fully expand after unsealing, which can take from 2 hours to 3 days, before measuring or testing.
- Accurate measurement of mattress dimensions is crucial; inspectors check multiple points to ensure compliance with manufacturer specifications.
- Rebound rate testing reveals how well a mattress returns to its original shape after compression, impacting comfort and support.
- Continuous improvement in QC processes helps reduce defects and enhances customer trust.
Importance of Mattress QC
Mattress Quality Standards
Mattress QC adheres to recognized international guidelines, such as ISO/FDIS 24975 and ISPA standards, which set clear expectations for quality and define acceptable measurement tolerances.
ISPA standards outline specific tolerance ranges:
- Mattresses up to 60 inches: Tolerance is +3/4 inch and -1/2 inch.
- Mattresses over 60 inches: Tolerance is +1 inch and -3/4 inch.
Manufacturers must consider material composition to meet these requirements. International regulations guide how companies test rebound rate and dimensional tolerance to ensure product safety and performance.
Impact of Vacuum Compression
Vacuum compression facilitates shipping but alters the physical properties of the foam. If a mattress remains compressed for too long, it may suffer permanent deformation. Foam density is critical; materials with a density of at least 1.8 lbs typically recover better. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines for expansion time is vital to protect quality.
Customer Satisfaction
Effective QC prevents issues like incorrect sizing or poor recovery, which lead to returns and complaints. Ensuring the product matches its description builds trust and loyalty.
Mattress QC Preparation
Unsealing and Inspection
Inspectors begin by carefully removing the vacuum packaging using blunt-edged tools to avoid fabric damage. An initial visual check identifies any immediate defects like tears or stains caused by shipping.
Expansion Time Guidelines
Proper expansion is a prerequisite for accurate testing. While initial expansion happens within minutes, full recovery takes time. Inspectors must wait for full expansion (typically 2 to 72 hours) before conducting measurements.
Recording Conditions
Environmental factors like temperature and humidity affect expansion rates. Inspectors record these conditions, along with the unsealing time, to contextualize the test results. Consistent documentation supports reliable quality checks.
Verifying Dimensional Tolerance
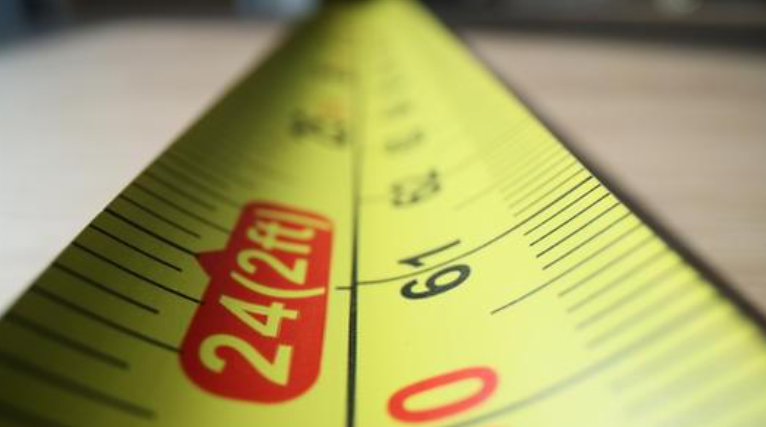

Measuring Mattress Dimensions
Once fully expanded, inspectors measure the length, width, and thickness using tape measures or digital calipers. Measurements are taken at multiple points to identify any warping or unevenness. Checking corners and edges for deformation is also standard procedure.
Tip: Measure on a flat, hard surface to prevent sagging and ensure accuracy.
Comparing to Specifications
Inspectors compare their measurements against the manufacturer's specifications. If the dimensions fall within the allowed tolerance, the mattress passes. Any deviation signals a potential issue with the vacuum process or material quality.
On-Site Testing Procedures
On-site testing follows strict protocols. The test room must accommodate the full mattress size and maintain stable environmental conditions.
| Testing Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Testroom Setup | Draft-protected, temperature and humidity controlled. |
| Conditioning | Mattress rests for 48 hours to fully recover. |
| Measurement | Inspectors measure all sides and surfaces post-conditioning. |
Rebound Rate Testing
Recovery and Restoring Mattress Shape
Rebound rate testing assesses the mattress's ability to return to its original shape. Vacuum compression collapses foam cells; recovery depends on material quality and compression duration. High humidity or low temperatures can hinder this process. QC teams look for full height recovery and firmness restoration.
Testing Methods and Equipment
Industry standards like ASTM F1566 guide performance testing. A common method is the ball drop test, where a ball is dropped from a set height (usually 500mm) to measure bounce back. This complies with DIN EN ISO 8307 and ASTM D3574 standards.
| Feature | Standard Specification |
|---|---|
| Compliance | DIN EN ISO 8307 / ASTM D3574 |
| Test Height | 500mm |
| Method | Measures rebound height of a free-falling ball |
Interpreting Results
Inspectors compare the rebound height against benchmarks. For instance, an average bounce of 16 inches might be the target. If the mattress fails to meet this, it may lack proper support. Documenting these results ensures that every shipped unit meets quality promises.
Best Practices for Mattress QC
Step-by-Step QC Checklist
A structured checklist ensures consistency:
- Unseal carefully and inspect for visible damage.
- Allow full expansion based on guidelines.
- Measure length, width, and thickness.
- Compare against specs and tolerances.
- Perform rebound rate testing.
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate reporting is key. Inspectors document unsealing times, environmental conditions, measurement data, and include photos of the process. This traceability helps identifying root causes of any defects.
Continuous Improvement
QC teams should regularly review protocols and collaborate with suppliers to address recurring issues. Data analysis from audits drives corrective actions, reducing defect rates over time.
Effective Mattress QC relies on a clear process: unseal, inspect, measure, and test. By verifying rebound rates and dimensional tolerances, manufacturers ensure compliance with quality standards, building brand trust and securing customer loyalty.
FAQ
How long should a mattress expand before testing?
Inspectors usually wait 2 to 72 hours for full expansion, depending on the manufacturer's specific instructions and the mattress type.
What tools are used for measuring mattresses?
Standard tools include tape measures, digital calipers, and laser distance meters to ensure precise readings of length, width, and thickness.
Why does rebound rate matter?
Rebound rate indicates the foam's resilience and ability to recover after compression. A high rate signifies better support, durability, and comfort for the user.
What if a mattress fails dimensional checks?
If a mattress falls outside the acceptable tolerance, it is flagged for review. The manufacturer must determine if it can be adjusted or if it needs to be rejected to maintain quality standards.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.