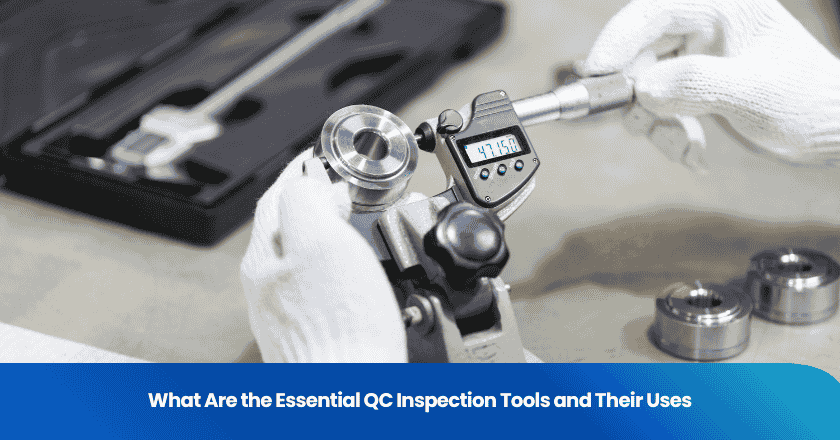
You need the right qc inspection tools to ensure product quality at every stage. Use calipers and micrometers for precise measurements. Select gauges and measuring tapes for quick checks. Rely on coordinate measuring machines for complex dimensions. Choose 3D scanners and imaging systems for fast, non-contact analysis. Apply surface and hardness testers to verify material properties. Automated testing systems help you speed up repetitive inspections. Pair these quality inspection tools with process tools to strengthen your quality control program.
Key Takeaways
- Use calipers and micrometers for precise measurements. They help maintain tight tolerances in your products.
- Incorporate automated testing systems to enhance efficiency. These systems reduce human error and improve accuracy.
- Select the right mix of contact and non-contact tools based on your needs. This ensures you get accurate measurements without damaging delicate components.
- Regularly calibrate your inspection tools to maintain reliability. Calibration helps avoid costly errors and ensures compliance with industry standards.
- Integrate inspection tools with digital quality management systems. This enhances traceability and supports data-driven decision-making.
QC Inspection Tools Overview
Quality inspection tools fall into several main categories, each serving a unique role in quality control.
You can see the primary classifications in the table below:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Analytical Tools | Tools for identifying and analyzing quality problems across industries. |
| Essential QC Tools | Tools that help in monitoring, controlling, and improving quality in production and service. |
| Pareto Chart | A bar chart that identifies the most significant causes of defects based on the 80/20 rule. |
Manual and Automated Tools
You use both manual inspection tools and automated systems to maintain high standards. Manual tools, such as rulers and calipers, give you direct control and flexibility. Visual inspection and basic measuring tools form the foundation of most quality inspection routines. These tools help you catch obvious defects and verify basic dimensions quickly.
- Manual inspections rely on human intuition and can be inconsistent and slow.
- Automated quality control systems enhance efficiency by detecting defects at unmatched speed.
- Automated systems minimize human error, achieving accuracy rates often exceeding 99%.
Automated quality inspection tools, such as vision systems and coordinate measuring machines, deliver consistent results and process large volumes of parts efficiently. You can use these systems to reduce inspection time and improve repeatability.
Contact and Non-Contact Tools
You choose between contact and non-contact quality inspection tools based on your application. Contact tools, like micrometers and dial gauges, physically touch the part to measure dimensions. Non-contact tools, such as 3D scanners and imaging systems, use lasers or cameras to capture measurements without touching the surface.
| Measurement Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Measurement | High accuracy and reliability; suitable for tight tolerances | Requires physical contact; not ideal for delicate or deformable components |
| Non-Contact Measurement | Faster data collection; effective for complex surfaces and fragile components | Slightly less accurate; may not be suitable for all applications |
You should select the right mix of quality inspection tools to match your process needs. By understanding these categories, you can build a robust quality control system that ensures product consistency and reliability.
Essential Inspection Tools
Calipers and Micrometers
You rely on calipers and micrometers for precise dimensional checks in your quality inspection process. Calipers offer versatility, allowing you to measure inside, outside, and depth dimensions quickly. You use them for general applications, such as woodworking and basic metalworking. Micrometers provide higher accuracy, reaching down to 0.0001 inches or 0.01 mm. You choose micrometers for tasks that demand exact measurements, such as machining and critical quality control steps. These essential inspection tools help you maintain tight tolerances and ensure that every part meets your specifications.
- Calipers give you flexibility for a wide range of measurements.
- Micrometers deliver unmatched precision for high-accuracy requirements.
Gauges and Measuring Tapes
You use gauges and measuring tapes to verify dimensions and material thickness in construction and manufacturing. Thickness gauges help you measure materials like rubber, films, and textiles, ensuring consistency and compliance with industry standards. Measuring tapes allow you to check lengths and widths quickly, making them indispensable for on-site inspections and routine quality control. These quality inspection tools support your efforts to maintain accuracy in automotive repair, diagnostics, and component evaluation.
Tip: Regularly calibrate your gauges and tapes to maintain measurement reliability.
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs)
Coordinate measuring machines play a vital role in your dimensional inspections. You use CMMs to capture complex geometries and verify critical tolerances. These machines provide consistent measurements, regardless of material properties or machining artifacts. CMMs maintain low relative error and high repeatability, even when surface conditions change. Compared to manual methods, CMMs deliver superior stability and accuracy, helping you meet strict quality control standards.
| Measurement Method | Standard Deviation (mm) | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CMM | < 0.0035 | < 0.013 |
| Manual (DVC) | 0.03333 | > 0.12 |
You find CMMs especially valuable in automotive and aerospace industries, where precision is critical.
3D Scanners and Imaging Systems
You turn to 3D scanners and imaging systems for fast, non-contact analysis of complex surfaces. These 3d quality inspection tools use lasers or cameras to capture detailed measurements without touching the part. In manufacturing quality control, you achieve typical accuracy ranges between 0.1 and 0.5 mm. For construction retrofitting, the range is 1 to 5 mm. Volumetric accuracy often reaches 2 mm plus 0.1 mm per meter. You use these quality inspection tools to inspect intricate shapes, verify assemblies, and document product geometry.
| Application Type | Typical Accuracy Range |
|---|---|
| Construction Retrofitting | 1-5 mm |
| Manufacturing Quality Control | 0.1-0.5 mm |
| Volumetric Accuracy | 2 mm + 0.1 mm/m |
You find these essential inspection tools especially useful in medical device and electronics industries, where non-contact measurement is required.
Surface and Hardness Testers
You use surface and hardness testers to evaluate material properties and ensure compliance with industry standards. Surface testers help you measure roughness and finish, which is crucial for automotive and aerospace components. Hardness testers, such as Rockwell, Brinell, and Vickers, allow you to assess the strength and durability of metals and other materials.
| Hardness Test | Common Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Rockwell | Automotive, aerospace, manufacturing | Quick results, suitable for various metals |
| Brinell | Foundries, construction, quality control | Ideal for rough surfaces, accurate for softer metals |
| Vickers | Laboratories, material science, research | Precise measurements for a wide range of materials |
You rely on these quality inspection tools to verify that your products meet required specifications and perform reliably in their intended applications.
Automated Testing Systems
Automated testing systems transform your quality inspection process by reducing human error and increasing consistency. You use these systems to detect defects in real time, ensuring that every product meets your standards. Automated systems minimize subjectivity and enhance accuracy, which is essential for maintaining high standards in manufacturing. You find these essential inspection tools especially valuable in medical device and automotive industries, where strict safety and quality requirements apply.
Automated systems help you comply with industry standards and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
You benefit from integrating traditional and advanced quality inspection tools. Combining in-process monitoring with post-process inspection streamlines nondestructive testing, improves defect identification, and reduces costs. Machine vision and automated inspection systems enhance predictive capabilities, saving significant labor costs and improving overall product quality.
Quality Control Tools for Process
Improvement
You need more than physical measurement devices to achieve consistent results in your inspection process. Quality control tools for process improvement help you monitor, analyze, and enhance your operations. These tools support defect identification, root cause analysis, and data-driven decision-making. The seven key quality control tools include:
1. Flow Charts and Process Maps
2. Check Sheets and Checklists
3. Histograms
4. Fishbone (Cause-and-Effect) Diagrams
5. Pareto Charts
6. Control Charts
7. Scatter Diagrams
Control Charts
You use control charts to track process stability over time. These charts help you distinguish between normal process variation and unusual events that require immediate action. By visualizing data trends, you can spot early signs of quality issues and take corrective steps before defects reach your customers. Control charts act as an early warning system in your inspection process, making them essential for maintaining product quality.
Check Sheets and Histograms
Check sheets give you a simple way to collect and organize data during inspections. You can count defects by category, record equipment stoppages, and track service requests. This structured approach ensures your data is complete and accurate. Histograms let you visualize data distribution, making it easier to spot trends and understand variation in your process. You can use these tools to identify opportunities for defect reduction and improve output consistency.
Tip: Use check sheets at the source to support real-time defect identification and analysis.
Pareto and Scatter Diagrams
Pareto diagrams help you prioritize quality issues by showing which problems have the greatest impact. You focus on the most significant causes, following the 80/20 rule. Scatter diagrams allow you to visualize relationships between two variables, helping you uncover patterns and root causes. The table below summarizes their roles:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Pareto Analysis | Focuses on the most significant issues, suggesting that 80% of problems come from 20% of causes. |
| Scatter Diagrams | Visualize correlations between two variables to identify potential root causes. |
Cause-and-Effect Diagrams
You use cause-and-effect diagrams to break down complex problems into manageable parts. This tool encourages teamwork and collaboration across departments. By identifying root causes, you can implement effective solutions and drive continuous improvement in your quality control program. These diagrams help you clarify issues and support systematic problem-solving.
When you combine these quality control tools with your quality inspection equipment, you create a comprehensive approach to defect identification and process improvement.
Selecting and Integrating Quality Inspection Tools
Tool Selection Factors
You need to choose the right inspection tools to support your quality control and quality assurance goals. Start by evaluating your current inspection challenges and identifying the features you require. Consider the following factors when selecting tools for different industries and applications:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Assess Your Current Inspection Challenges | Identify challenges in current processes to narrow down options. |
| Evaluate Must-Have Features | List important features like customizable checklists and real-time data capture. |
| Check for Real-Time Reporting | Ensure the system generates detailed reports for monitoring inspections. |
| Verify Integration with Other Tools | Confirm compatibility with ERP, CRM, and other business applications. |
| Research Vendor Reputation | Choose solutions with a proven track record and positive reviews. |
| Consider Cost Savings | Evaluate total cost of ownership, including maintenance. |
| Assess Vendor Support and Training | Look for extensive support and training resources. |
| Check Scalability and Customization | Ensure the system can grow and adapt with your business needs. |
Selecting the right tools improves accuracy, completeness, and consistency in your quality control process. You also reduce manual data cleaning and improve decision accuracy.
Calibration and Maintenance
You must keep your inspection tools calibrated and well-maintained to ensure reliable results in both quality control and quality assurance. Follow these best practices:
- Schedule annual calibrations for equipment like CMMs.
- Wear gloves and monitor temperature to maintain a stable environment during calibration.
- Use multiple calibration artifacts and specialized setup tools for accuracy.
- Pair calibration with annual preventative maintenance to tune and inspect equipment.
Regular calibration reduces measurement errors, extends equipment lifespan, and ensures compliance with safety standards.
Integration with Quality Systems
Integrating your inspection tools with digital quality management systems enhances traceability and reporting. You benefit from real-time data collection, automated reporting, and seamless integration with other business systems. Customizable checklists and photo capture improve inspection accuracy. Real-time data entry ensures your information stays up-to-date and reliable. This integration supports data analysis, helping you identify trends and drive continuous improvement in quality assurance and quality control.
Tip: Address challenges such as resistance to change and inadequate training by providing clear communication and ongoing support during integration.
You achieve the highest quality standards by using a balanced mix of essential QC inspection tools and process improvement methods.
- A diverse toolkit helps you prevent defects and streamline compliance, reducing the risk of costly recalls.
- Regular calibration and careful tool selection ensure accuracy, safety, and cost savings.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Guarantees precise readings, reducing errors in critical measurements. |
| Compliance | Meets international standards and supports ongoing improvement. |
Assess your current tools, involve your team, and commit to continuous upgrades for lasting quality success.
FAQ
What are the most common inspection tools in quality control for manufacturing?
You use calipers, micrometers, and gauges as the most common inspection tools in quality control. In manufacturing, these tools help you measure dimensions, thickness, and surface finish. You rely on them to maintain product consistency and meet industry standards.
How do inspection tools in quality control improve manufacturing efficiency?
Inspection tools in quality control help you detect defects early in manufacturing. You reduce waste and rework by identifying issues before products move to the next stage. These tools streamline your process and ensure you meet customer requirements.
Why should you calibrate inspection tools in quality control regularly in manufacturing?
You must calibrate inspection tools in quality control to maintain accuracy in manufacturing. Regular calibration ensures your measurements remain reliable. You avoid costly errors and keep your manufacturing process compliant with industry regulations.
Can you use automated inspection tools in quality control for all manufacturing processes?
You can use automated inspection tools in quality control for many manufacturing processes. These tools work best in high-volume environments. You may still need manual inspection tools in quality control for unique or complex manufacturing tasks.
How do you choose the right inspection tools in quality control for your manufacturing needs?
You assess your manufacturing process and product requirements. You select inspection tools in quality control based on measurement range, accuracy, and application. You consider the environment and the skill level of your team to ensure the best fit for your manufacturing operation.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.





