In the technical assessment of load-bearing Softline Products, the structural fidelity of the shoulder strap junction and the efficacy of environmental barriers are the primary determinants of a product's operational lifecycle. High-performance outdoor backpacks must maintain their mechanical integrity under erratic dynamic loads while simultaneously protecting the internal payload from hydrostatic pressure ingress. Engineering excellence in this domain is validated through rigorous metrological standards, ranging from tensile seam rupture analysis to accelerated weathering simulations. By adhering to international benchmarks such as ISO 13934 and ASTM D5034, manufacturers can ensure that their technical designs—from ultralight trekking packs to heavy-duty tactical rucksacks—meet the stringent durability requirements of the professional outdoor market.

Key Takeaways
- Shoulder strap junction integrity is quantified by tensile pull-off force (N), with industrial benchmarks requiring resilience up to 500N for heavy-duty packs.
- Waterproof performance is measured by 'Hydrostatic Head' (HH) pressure, where high-performance rain covers must exceed 10,000mm ratings.
- Material metrology includes 'Denier' density and 'Tear Strength' (ASTM D2261) to prevent rip-propagation in high-abrasion environments.
- Standardized quality checks must identify 'Seam Grinning' and 'Needle Cutting' defects before shipment.
- Durable Water Repellent (DWR) coatings are chemically evaluated for wash-fastness to ensure multi-season functionality.
- Real-time digital reporting via quality assurance protocols provides traceability across global manufacturing hubs.
The Mechanics of Load Distribution and Seam Stress
The shoulder strap attachment point is the focus of intense shear and tensile stress. In a typical 30-liter hiking pack carrying a 10kg load, the static gravitational force is compounded by dynamic 'Bounce' during movement, creating instantaneous loads that can reach triple the static weight. For industrial-grade outdoor gear quality control, the objective is to determine the 'Breaking Point' of the seam-to-substrate interface.
Physics of Stitching: Lockstitch vs. Bar-Tacking
Technical durability is achieved through 'Geometric Redundancy.' While a standard lockstitch provides basic closure, professional-grade backpacks utilize 'Box-and-Cross' or high-density 'Bar-Tacking' at the strap anchor. This construction method increases the number of 'Anchorage Points' per square centimeter, distributing the load across a wider area of the fabric matrix to prevent the 'Postage Stamp' effect, where the needle punctures themselves act as a perforation line for tearing.
| Stitch Method | Technical Objective | Common Application | Force Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lockstitch | General panel closure | Internal pocketing | Low - Moderate |
| Bar-Tacking | High-density reinforcement | Strap-to-body junctions | High (350N+) |
| Box-and-Cross | Torsional stress distribution | Top haul handles | Extreme (500N+) |
| Welded Seam | Zero-puncture monolithic bond | Dry bags, premium rain packs | Variable (Chemical Bond) |
Quantitative Tensile Strength Validation: ISO 13934 Protocols
Laboratory validation of seam strength requires the elimination of human visual subjectivity. Technicians utilize a Universal Testing Machine (UTM) equipped with specialized jigs. The protocol involves the 'Grab Test' (ASTM D5034) or the 'Strip Test' (ISO 13934-1), where a constant rate of extension—typically 100mm/min—is applied until structural failure occurs.
Metrological Evaluation of Junction Strength
A professional manufacturing quality inspection should identify two distinct failure modes: 'Thread Rupture,' indicating the sewing thread is the weak link, and 'Fabric Failure,' where the strap pulls the yarns out of the body fabric. For technical hiking gear, a minimum threshold of 45kg (440N) per strap is often the technical requirement for export-grade compliance.
Technical Standard Note: UV exposure is a primary catalyst for 'Fiber Embrittlement.' Professional labs often perform tensile testing *after* 100 hours of UV-C weathering to ensure that the rucksack won't lose 50% of its strength during a single high-altitude expedition.
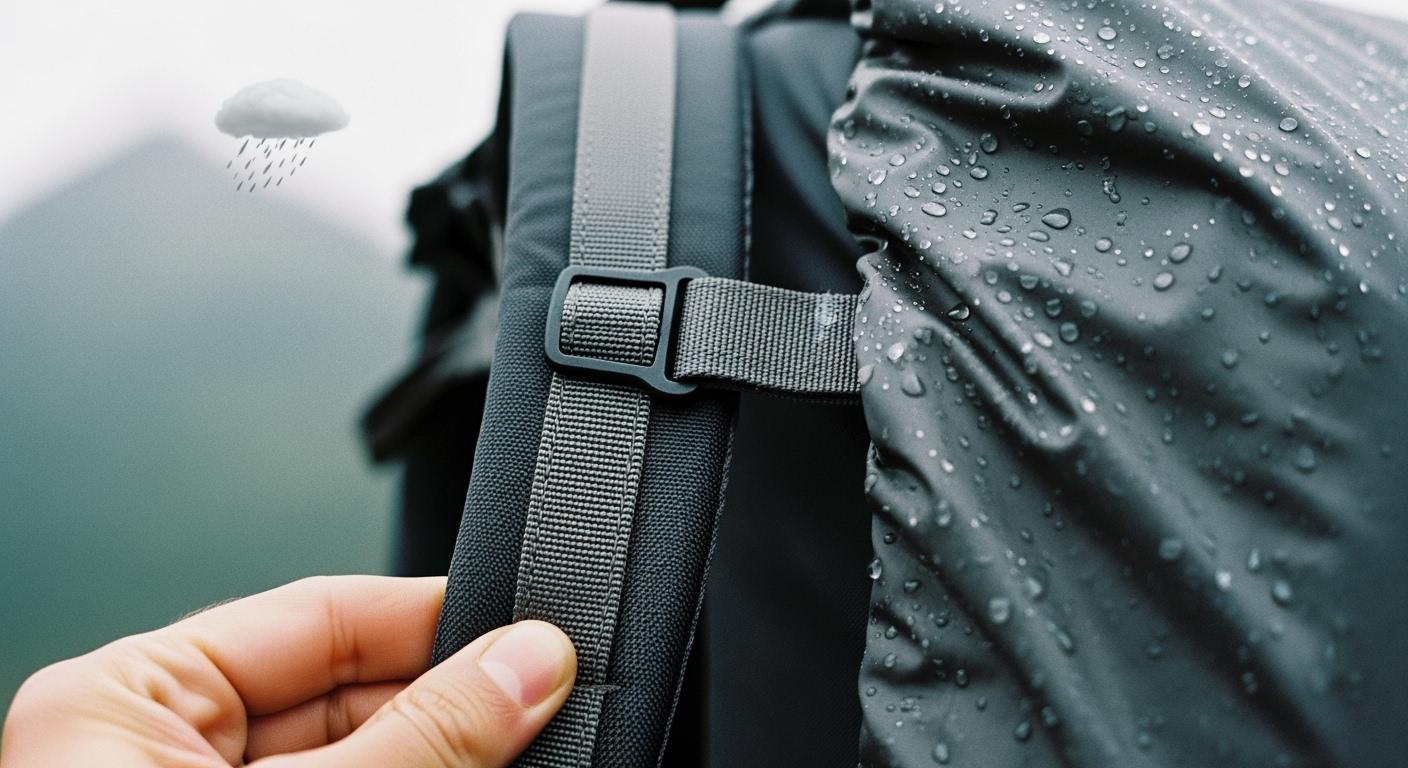
The Engineering of Waterproof Performance: Rain Cover Analysis
Waterproof integrity in backpacks is achieved through a multi-tier system: the DWR coating on the exterior, an internal PU (Polyurethane) or TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) laminate, and seam-sealing tape. The definitive technical metric for this barrier is the 'Hydrostatic Head' (HH) rating, measured in millimeters of water column height.
Hydrostatic Head Dynamics (ISO 811)
During a hydrostatic pressure test, a circular fabric specimen is subjected to increasing water pressure. A rating of 1,500mm is the technical minimum to be called 'Waterproof,' but for rain covers exposed to wind-driven rain, a rating of 3,000mm to 5,000mm is required. Expedition-grade gear utilizing TPU laminates often exceeds 10,000mm, ensuring that even under the pressure of a shoulder strap (which 'squeezes' water through), the gear remains dry.
| Performance Grade | HH Rating (mm) | Technical Feature | Ideal Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-Resistant | 600 - 1,200 | DWR Finish only | Light mist, urban drizzle |
| Standard Waterproof | 1,500 - 3,000 | PU Coating + Taped Seams | Day hiking, standard rain |
| Technical/Expedition | 5,000 - 10,000 | TPU Laminate + Welded joints | High-altitude storms, snow |
| Submersible (IPX7) | 20,000+ | Non-breathable heavy vinyl | River crossings, kayaking |
Practical Quality Control: From PPI to PSI
Consistency in high-volume production is achieved by integrating production management protocols into every stage. A simple pre-shipment check is insufficient for safety-critical Softline goods. Effective oversight requires:
- Pre-Production (PPI): Testing the 'Warp-to-Weft' yarn ratio and DWR bead angle of the raw fabric lot.
- During Production (DPI): Daily 'Needle Inspection' to ensure no fragments are trapped and that needle-heat hasn't melted synthetic fibers during high-speed sewing.
- Pre-Shipment (PSI): Final random sampling for whole-bag 'Handle Pull-off' and 'Zipper Endurance' (ISO 16181) to verify assembly fidelity.
Material Science: Selecting High-Tenacity Polymers
The ultimate limit of durability is determined by the fiber denier and yarn orientation. While 1000D Cordura nylon is the industrial standard for abrasion, modern 'Ripstop' patterns utilize high-tenacity 'Grid-lines' to stop a puncture from propagating into a structural tear. Quality control must verify the 'Denier' density through gravimetric analysis, ensuring the vendor has not substituted 420D nylon where 600D was specified—a common form of 'Quality Fade' in mass production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a "Waterproof" and "Water-Resistant" backpack?
Technically, water-resistant gear relies on a DWR surface coating that makes water bead up, but the material remains porous. A waterproof backpack utilizing a TPU membrane and sealed seams provides a continuous physical barrier that can resist liquid penetration even under high hydrostatic pressure.
Why do shoulder straps often fray at the edges?
This is typically a technical failure in 'Edge Finishing.' If the nylon webbing is cut with a cold blade rather than a laser or hot-knife, the filament ends are not fused, leading to rapid unraveling under the kinetic stress of walking. Industrial product inspections specifically check for 'Fused Edge' compliance.
How long should a DWR coating last?
The technical durability of DWR is measured in 'Wash Cycles' (e.g. 20 washes). Over time, abrasion and dirt clog the microscopic polymer 'hairs' that repel water. Professional maintenance requires the re-application of a spray-on DWR every season to maintain the surface tension necessary for rain bead-up.
What is a 'Seam Tape Peel Test'?
This involve measuring the force in Newtons required to peel the heat-sealed tape from the fabric. A high-quality bond must exceed 10N/cm. If the factory uses an incorrect 'Dwell Time' or temperature on the sealing machine, the tape will fail in cold or humid environments.
Can I rely on a backpack with a "100% Waterproof" claim?
Technically, no bag with a standard zipper is 100% waterproof if submerged. Look for the 'IPX Rating.' IPX4 indicates resistance to heavy splashes; IPX7 indicates the ability to be fully submerged for 30 minutes. Most high-performance hiking packs are IPX4 or IPX5 rated when paired with a rain cover.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.