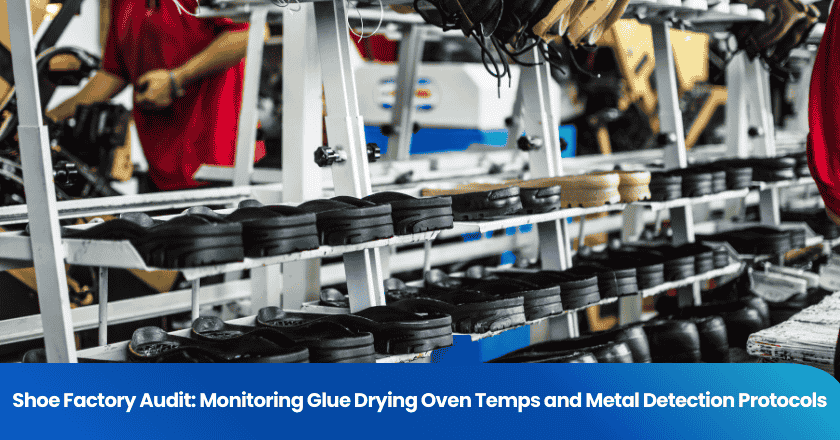
The technical validation of a footwear manufacturing facility is a complex process centered on mitigating latent structural risks. For industrial stakeholders and global brands, a shoe factory audit is the primary mechanism for ensuring that mass-production lines adhere to the exacting standards set during the prototyping phase. Two critical control points dominate the technical audit: the precise thermal management of glue drying ovens and the implementation of zero-tolerance metal detection protocols. A failure in adhesive curing can lead to catastrophic sole delamination, while undetected metal fragments pose a severe physical hazard to consumers. This guide explores the mechanical engineering and safety metrology required to maintain a compliant and high-performance production environment.

Key Takeaways
- Oven temperature stability (typically 50'C - 60'C) is mandatory for the cross-linking kinetics of PU adhesives.
- Metal detection protocols utilize a 9-point calibration system to eliminate electromagnetic dead zones in the conveyor tunnel.
- Standardized quality checks must identify 'Cold Bonds' caused by inconsistent thermal activation.
- Manufacturing audits for Softline products emphasize 'In-Process' traceability rather than just final inspections.
- Professional quality assurance relies on digital time-stamped reporting for real-time risk mitigation.
- Compliance with ISO 9001 and SLCP frameworks ensures structural quality and social responsibility in the supply chain.
The Metrology of Adhesion: Glue Drying Oven Control
In footwear assembly, the interface between the upper and the outsole is the most stressed component. Modern manufacturing primarily utilizes Polyurethane (PU) adhesives due to their superior bond strength and flexibility. However, PU adhesives are highly sensitive to the 'Heat Activation' phase. Technical auditors must verify that the factory's drying range provides a uniform thermal profile across the entire length of the conveyor.
Physics of PU Heat Activation
The technical objective of the glue oven is two-fold: first, to evaporate the organic solvents (or water in eco-adhesives), and second, to trigger the 'Molecular Cross-linking.' Most industrial cements require a surface temperature of 55'C +/- 5'C. If the temperature is too low, the adhesive remains in a 'Tacky' state without structural depth; if too high, the polymer chains may suffer from thermal degradation, leading to brittle failure. During a shoe manufacturing audit, infrared thermometers are used to map the actual shoe surface temperature inside the oven.
| Adhesive Type | Technical Objective | Ideal Activation Range | Critical Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent-Based PU | Rapid solvent flash-off | 50'C - 55'C | Incomplete solvent removal |
| Water-Based PU | Evaporative cross-linking | 60'C - 65'C | Hydrolytic instability |
| Hot-Melt Adhesives | Flow-state transformation | 80'C - 100'C | Thermal substrate warping |
| Primers (UV-Cured) | Surface energy modification | UV Irradiation | Interfacial delamination |
Zero-Tolerance Metal Detection Protocols
Metal contamination, typically originating from broken sewing needles, staples, or machinery pins, represents a 'Critical Defect' with zero tolerance in the footwear industry. A technical audit must verify the efficacy of the factory's 'Broken Needle Policy' (BNP). This includes a mandatory machine stoppage and a fragment-recovery log. Subsequently, every pair of shoes must pass through a conveyorized metal detector before final packaging.
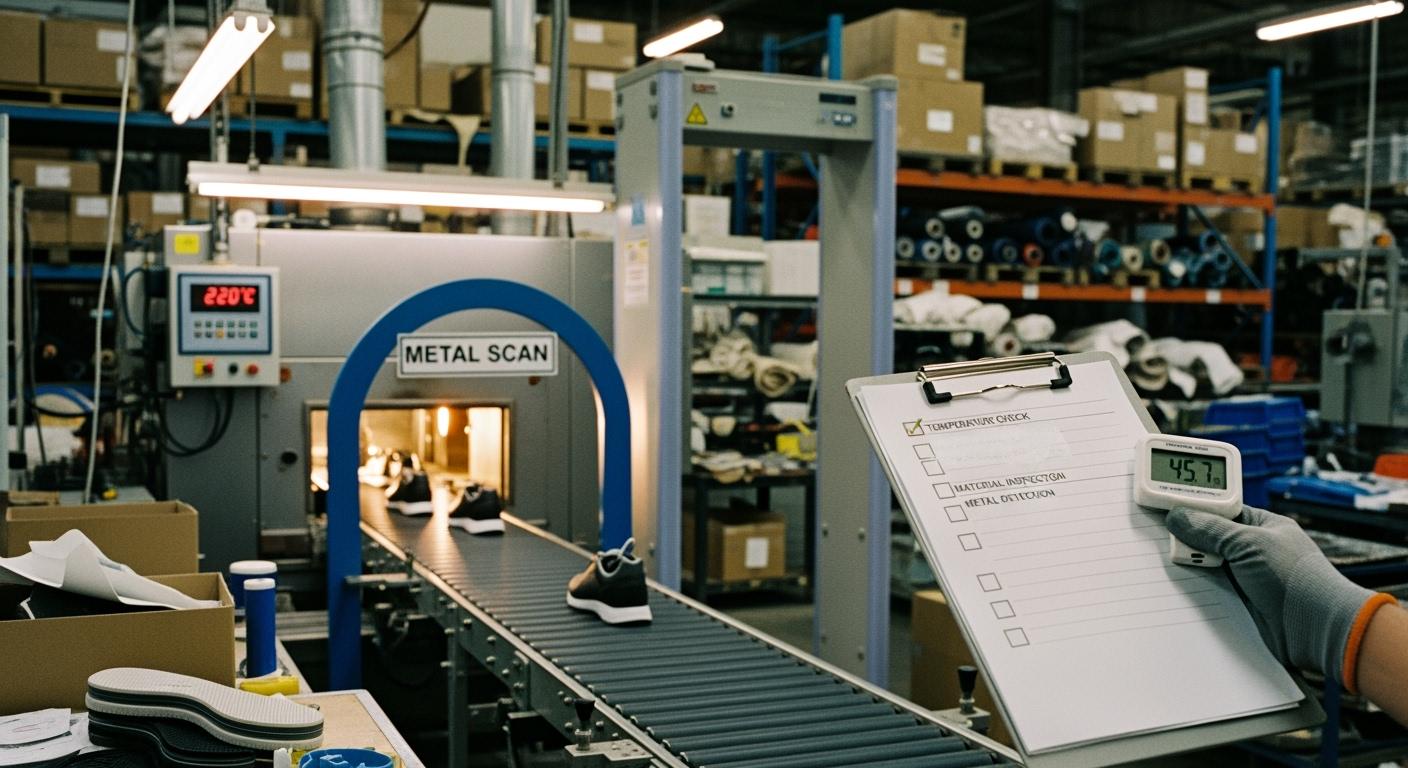
The 9-Point Calibration Method
The accuracy of a metal detector is not uniform; the magnetic field is typically weakest at the corners and top of the tunnel. During a manufacturing site inspection, technicians perform a 9-point test. A test card containing a 1.0mm ferrous sphere is passed through nine distinct zones (Left, Center, Right at Top, Middle, and Bottom). If the detector fails to trigger at any of these points, the sensitivity is technically insufficient, and the entire production batch since the last valid check must be re-inspected.
Technical Standard: For children's footwear, the sensitivity threshold is often tightened to 0.8mm ferrous and 1.2mm non-ferrous (e.g. aluminum or brass) to ensure total protection against microscopic sharp fragments.
Operational Quality Management and Audit Customization
Reliability is built into the 'Workflow Logic' of the factory. An audit assesses the mill's Quality Management System (QMS), focusing on the 'Correction Action Plan' (CAP) implementation. For large OEM contracts, audits must be customized to address the specific material properties of the order. For example, a shoe using high-moisture natural leather requires different warehouse humidity controls than a synthetic mesh sneaker.
Technical benchmarks for industrial audits include:
- SOP Fidelity: Ensuring the workers follow the 'Two-Coat' glue application standard consistently.
- Press Pressure Calibration: Verifying that sole presses apply the required 3.5 - 4.5 kg/cm2 to ensure bond compaction.
- Humidity Oversight: Maintaining a relative humidity below 60% in the material storage area to prevent fungal germination (mold).
| Audit Dimension | Industrial Benchmark | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment State | ISO 9001 Compliant | Maintenance logs and sensor calibration |
| Process Control | Standardized SOPs | Direct workshop observation and batch logs |
| Social Compliance | SLCP / BSCI Framework | Worker interviews and labor record audits |
| Material Integrity | Traceable MTRs | Chemical batch testing and SGS reports |
Digital Transparency and Real-Time Reporting
Modern quality assurance has transitioned from paper checklists to digital ecosystems. On-site inspectors utilize mobile platforms to upload 360-degree photos and videos of the oven sensors and metal detection cycles. This real-time visibility allows global buyers to intervene instantly if a technical discrepancy is identified. Effective production monitoring ensures that the 'Lasting' and 'Bottoming' stages are performed under controlled conditions, preventing the 'Quality Fade' often associated with accelerated production timelines.
Furthermore, digital logs provide 'Process Traceability.' If a batch of shoes suffers from delamination in the retail market six months later, the digital audit record allows the brand to review the exact oven temperature and glue batch used on that specific day, facilitating precise root-cause analysis.
Practical Guide for Professional Procurement
When conducting an industrial evaluation of a potential vendor, the following technical indicators serve as reliable proxies for quality capability:
- Climate-Controlled Warehouse: A factory that controls ambient moisture is significantly less likely to deliver mold-infested footwear.
- Automated Adhesive Dispensing: Reduces human error in the mix ratio of hardeners and resins.
- In-Line Laboratory: The presence of on-site tensile and flex-testing machines indicates a commitment to empirical quality validation.
- 9-Point Calibration Proof: Ask the operator to perform a 9-point metal detection test in your presence; an untrained response indicates a major compliance risk.
Integrating these technical checks into a systematic facility audit protects the brand's financial interests and ensures that the final consumer receives a safe, durable, and structurally sound product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary cause of sole delamination?
Technically, most bond failures are due to improper 'Surface Priming' or inadequate 'Heat Activation.' If the outsole material (like EVA) is not chemically primed to increase its surface energy, the PU glue cannot form a molecular bond, leading to a 'Peel Failure' even if the oven temperature was correct.
How often should a metal detector be calibrated?
For industrial quality control, a metal detector should undergo a standard 'Go/No-Go' check at the start of every shift and a comprehensive 9-point technical calibration every 1-2 hours to ensure magnetic field stability.
Does a higher oven temperature dry glue faster?
While it accelerates solvent evaporation, excessive heat can cause 'Surface Hardening,' where a dry crust forms on the glue while the interior remains wetted. This technically reduces bond strength. Consistency and duration (dwell time) are more important than peak temperature.
Can I trust a factory with only an ISO 9001 certification?
ISO 9001 proves the factory has a documented management *system*, but it does not technically certify the *product* quality. A professional footwear audit must supplement ISO certificates with technical process checks like glue-pull tests and abrasion analysis.
What is the SLCP framework in shoe audits?
The Social & Labor Convergence Program (SLCP) is a technical tool used to verify social and labor conditions without the need for multiple redundant audits. It provides a standardized data set that can be shared across multiple global brands, ensuring transparency in worker safety and ethics.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.